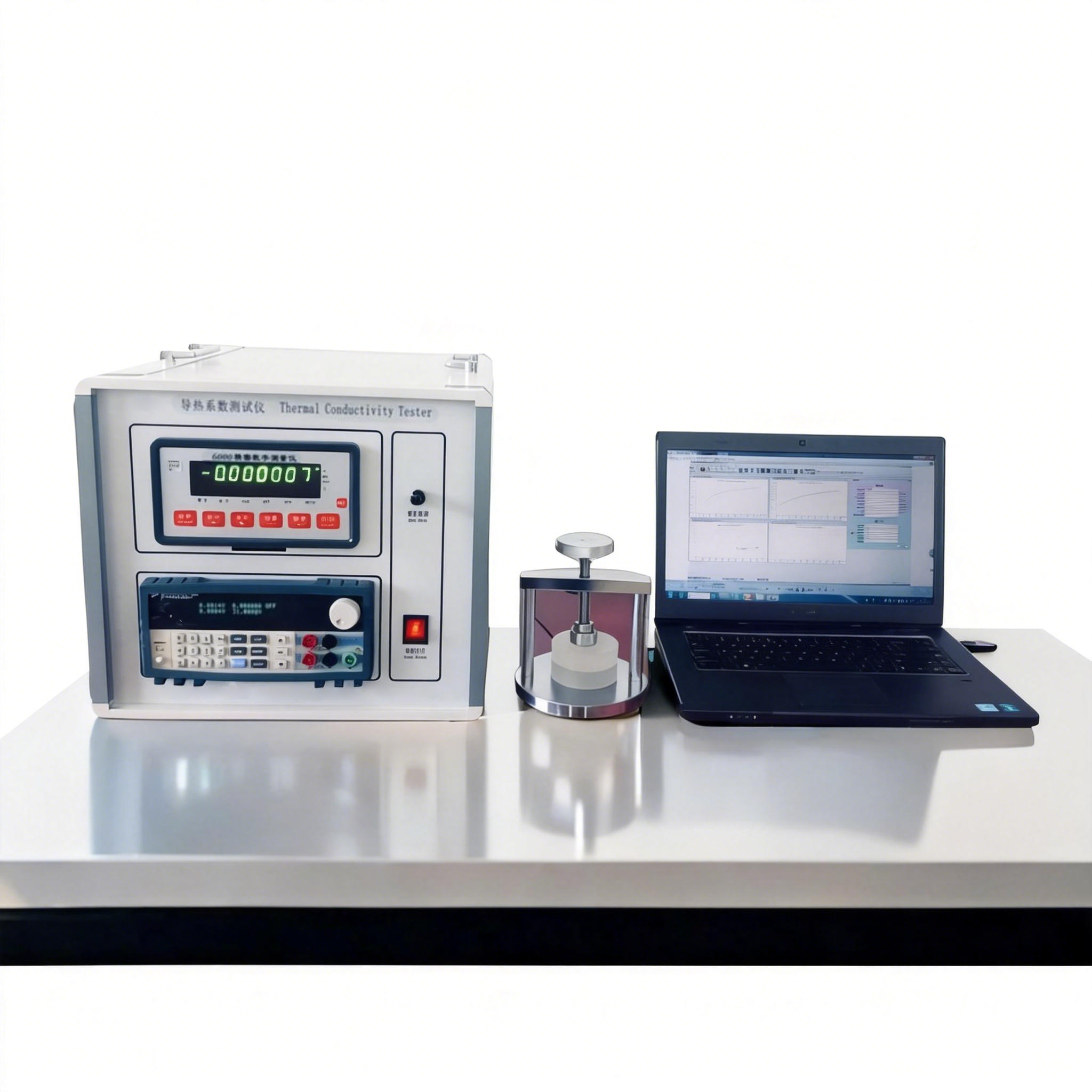
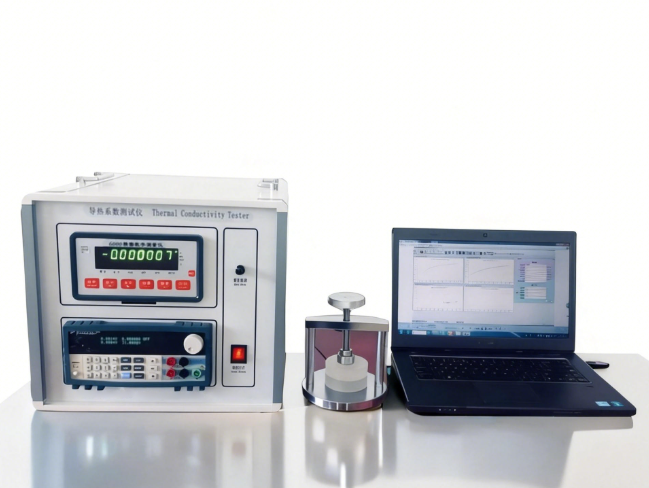
Multi-Function Thermal Constants Analyzer
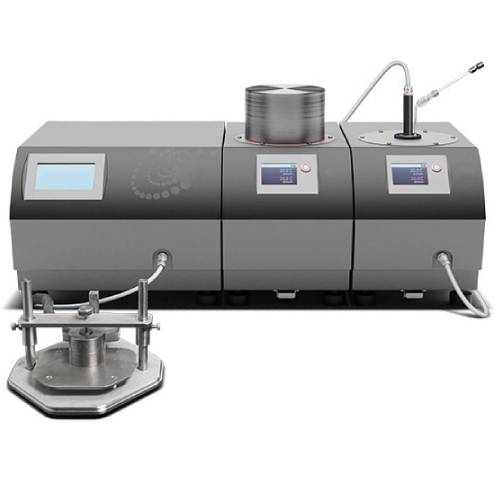

Multi-Function Thermal Constants Analyzer is a versatile analytical instrument designed for accurate measurement of absolute thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat capacity, and thermal effusivity of solids, liquids, pastes, and powders. By integrating multiple transient measurement methods within a single platform, the system supports comprehensive thermal characterization across a wide range of materials and temperature conditions, making it suitable for both research and standardized testing applications.
Application
The Multi-Function Thermal Constants Analyzer is used for quantitative thermal property evaluation in various material forms and industries, including:
Polymers, composites, and construction materials
Liquids, phase-change materials, and coolants
Pastes, powders, and bulk solids
Soil, polymers, and anisotropic materials
Typical test samples include solid plates, bulk materials, liquids in containers, pastes, powders, and soil samples, depending on the selected measurement method.
Standards
The analyzer supports multiple internationally recognized test methods and standards, including:
(1) ISO 22007-2: Plastics — Determination of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity — Transient plane heat source method
(2) ISO 22007-7: Plastics — Determination of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity using transient plane heat source
(3) GB/T 32064: Transient plane heat source method for thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of building materials
(4) ASTM E3088: Standard test method for determination of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity using the transient plane source method
(5) ASTM D7896: Transient hot-wire method for thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and volumetric heat capacity of liquids
(6) ASTM D5334: Transient line-source probe method
(7) ASTM D5930: Determination of thermal conductivity of plastics by transient line-source technique
(8) IEEE 442: Soil thermal resistivity measurement
Parameters
| Method | TPS | THW | MTPS | THS | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applicable Materials | Solids, pastes, powders | Liquids, phase-change materials | Solids, pastes, powders | Solid rectangular samples | Soil, pastes, polymers |
| Measurement Mode | 3D bulk, anisotropic, plate, thin film, 1D | Bulk | 3D bulk, anisotropic, plate, 1D | Bulk, anisotropic | Bulk |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 0.005–2000 | 0.01–2 | 0.03–500 | 0.01–2 | — |
| Thermal Diffusivity (mm²/s) | 0.01–1200 | Up to 0.5 | 0.01–300 | Up to 0.5 | — |
| Volumetric Heat Capacity (MJ/m³·K) | Up to 5 | Up to 5 | Up to 5 | Up to 5 | — |
| Thermal Effusivity (W·s½/m²·K) | 5–60000 | Not applicable | 20–40000 | Not applicable | — |
| Contact Thermal Resistance (m²·K/W) | Measured | Not applicable | Measured | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Sample Thickness (mm)* | ≥0.01 | — | ≥0.1 | — | — |
| Test Time (s) | 0.25–2560 | 1 | 0.25–2560 | 0.25–2560 | 180 |
| Accuracy (Thermal Conductivity) | 3% | 2% | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| Repeatability (Thermal Conductivity) | 1% | 1% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Temperature Range (°C)** | 0 to 300 / up to 750 or 1000 | 10 to 200 | 0 to 100 / −50 to 200 | −75 to 300 | −40 to 100 |
| Sample Configuration | Symmetric / asymmetric | Insert type | Asymmetric (single-sided) | Symmetric / asymmetric | Insert type |
Features
Supports multiple transient methods within one integrated system
Measures absolute thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat, and thermal effusivity
Suitable for solids, liquids, pastes, powders, and soil samples
Wide thermal conductivity and temperature measurement ranges
Direct measurement of sensor–sample contact thermal resistance for improved accuracy
Accessories
(1) Transient plane heat source (TPS) sensors
(2) Transient hot-wire (THW) sensors
(3) Modified transient plane source (MTPS) sensors
(4) Transient hot strip (THS) sensors
(5) Transient line source (TLS) probes
(6) Sample holders for solid, liquid, and soil configurations
Test Procedures
Select the appropriate measurement method based on sample type and test requirements.
Prepare and position the sample according to the selected method and configuration.
Place the corresponding sensor in contact with or within the sample as required.
Set test parameters such as temperature range and measurement time.
Initiate the test; transient thermal signals are generated and recorded automatically.
The system calculates thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat, and related properties based on the acquired data.
Maintenance Information
Keep all sensors clean and free from surface contamination to ensure stable contact conditions.
Periodically inspect sensor surfaces for wear or damage, especially when testing rough samples.
Verify calibration and system performance at regular intervals using reference materials.
Store sensors and probes in protective containers when not in use to prevent mechanical damage.
FAQ
1. What thermal properties can the Multi-Function Thermal Constants Analyzer measure?
The analyzer is designed to measure absolute thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, volumetric specific heat capacity, and thermal effusivity. By using different transient methods such as TPS, THW, MTPS, THS, and TLS, it can characterize these properties for solids, liquids, pastes, powders, and soil. This multi-parameter capability allows a comprehensive understanding of heat transfer behavior under various material conditions.
2. How does the analyzer support different material forms?
Different transient measurement methods are integrated into the system to match specific material types. TPS and MTPS are mainly used for solids, pastes, and powders, while THW is suitable for liquids and phase-change materials. TLS probes are commonly applied to soil and polymer testing. Each method uses a dedicated sensor configuration, ensuring appropriate contact conditions and reliable thermal response for accurate measurements.
3. What standards are supported by this instrument?
The system supports several international standards, including ISO 22007-2 and ISO 22007-7 for plastics, GB/T 32064 for building materials, ASTM E3088 for transient plane source measurements, ASTM D7896 for liquid thermal properties, and ASTM D5334 and ASTM D5930 for transient line source methods. These standards make the analyzer suitable for both research and standardized testing environments.
4. Why is contact thermal resistance measurement important?
For solid samples, the analyzer can directly measure the contact thermal resistance between the sensor and the sample surface. This is important because surface roughness and contact conditions can significantly influence heat transfer results. By quantifying this resistance, the system improves the reliability of measured thermal conductivity and related parameters, especially when comparing materials with different surface finishes.
Leave Message Get Price