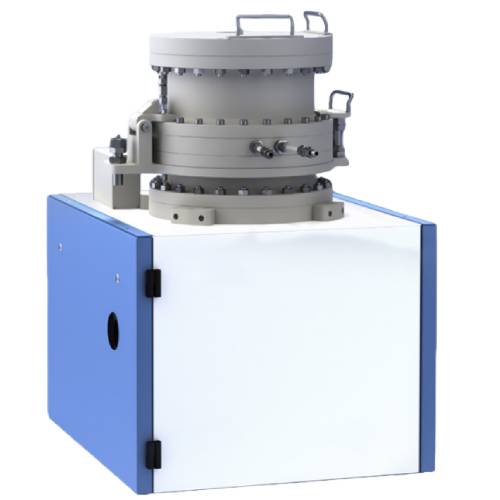
Rolling Contact Fatigue Tester
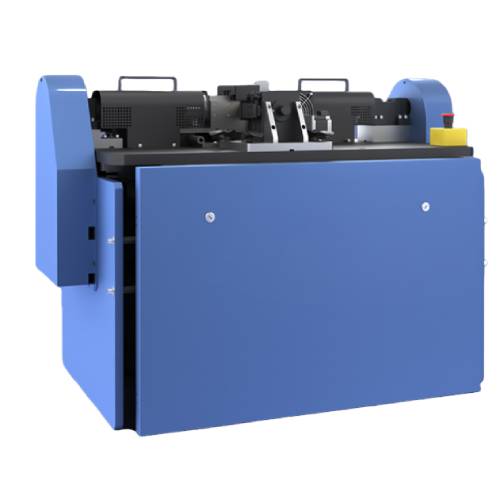

Rolling Contact Fatigue Tester is a specialized testing system designed to investigate traction, wear, and rolling contact fatigue under controlled rolling and sliding conditions. The tester evaluates material behavior under alternating surface stress fields that lead to crack initiation and material removal. Featuring an open-platform architecture, dual independently controlled high-torque servo motors, and servo-driven loading, the system delivers high repeatability and precise measurement for rolling contact fatigue studies in lubricant, automotive, railway, and aerospace applications.
Application
Rolling Contact Fatigue Research
Evaluation of rolling contact fatigue (RCF) under pure rolling, pure sliding, and combined rolling–sliding conditions.
Traction and Wear Analysis
Measurement of traction force and wear behavior at different rolling–sliding ratios.
Lubricant Performance Evaluation
Assessment of lubricant influence on rolling contact fatigue, wear evolution, and surface damage mechanisms.
Automotive and Rail Components
Testing of bearings, gears, wheels, and rails under realistic rolling contact conditions.
Aerospace and Turbine Components
Reliability assessment of rolling elements and transmission components subjected to cyclic contact stresses.
Standards
GB/T 10622 Rolling Contact Fatigue Test Method for Metallic Materials
JB/T 10510 Contact Fatigue Test Method for Rolling Bearing Materials
ASTM D6121 Standard Test Method for Rolling Contact Fatigue of Metals and Alloys
Parameters
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Maximum Load | Up to 8000 N (customizable) |
| Load Control | Real-time servo-controlled loading |
| Speed Control | Real-time speed control |
| Drive System | High-power servo motors |
| Temperature Range | −35 °C to 150 °C |
Features
Capability for pure rolling, pure sliding, and rolling–sliding combinations
Servo-controlled loading system for precise force application
Environmental control for temperature-dependent testing
Support for multiple specimen configurations
Online three-dimensional optical inspection
Real-time monitoring of friction and wear behavior
Accessories
(1) Rolling contact specimen holders
(2) Servo-driven loading module
(3) Environmental temperature control chamber
(4) Online 3D optical inspection module
(5) Friction and wear monitoring sensors
Test Procedures
Install the selected rolling contact specimens and configure the rolling–sliding ratio.
Set test parameters including load, speed, temperature, and rolling condition.
Initiate the servo-controlled loading and motion sequence.
Monitor traction, friction, and wear behavior in real time during testing.
Complete the test cycle and perform post-test analysis using online optical inspection data.
Maintenance Information
Periodic inspection of servo motors and loading components is recommended to maintain stable operation.
Specimen holders and contact surfaces should be cleaned after each test to ensure consistent contact conditions.
Environmental control components should be verified regularly to maintain temperature accuracy.
Optical inspection and friction monitoring systems should be checked to ensure long-term measurement reliability.
FAQ
1. What is the primary purpose of the Rolling Contact Fatigue Tester?
The Rolling Contact Fatigue Tester is designed to study traction, wear, and rolling contact fatigue under controlled rolling and sliding conditions. Rolling contact fatigue is a failure mechanism caused by alternating stress fields at the surface, typically leading to crack initiation and material removal. This tester enables systematic investigation of how rolling–sliding ratios, load, temperature, and lubrication conditions influence fatigue life and wear behavior. It is particularly important for evaluating components used in high-speed trains, electric vehicles, and turbines, where rolling contact fatigue plays a critical role in service reliability.
2. What types of motion and contact conditions can be simulated?
The tester supports pure rolling, pure sliding, and combined rolling–sliding conditions. By adjusting the independently controlled servo motors, different rolling–sliding ratios can be achieved to simulate real operating conditions. This flexibility allows the system to replicate contact states encountered in bearings, gears, wheels, and rails, providing comprehensive insight into traction behavior, wear evolution, and rolling contact fatigue mechanisms.
3. How does the tester ensure accurate and repeatable results?
High repeatability is achieved through servo-controlled loading, real-time control of load and speed, and an advanced control system. The open-platform architecture simplifies specimen installation and alignment, while high-torque servo motors maintain stable motion throughout the test. These features, combined with online friction, wear, and three-dimensional optical monitoring, ensure precise measurement and consistent test results across repeated experiments.
4. Which industries commonly use rolling contact fatigue testing?
Rolling contact fatigue testing is widely used in the bearing and gear industry, aerospace engineering, railway systems, and automotive manufacturing. Typical applications include evaluating bearing steels, gear materials, engine and transmission components, rails, and wheels. The tester supports material optimization and reliability assessment for components subjected to cyclic rolling contact stresses.
Leave Message Get Price