Textile burning performance oxygen index test method

The commonly used methods for evaluating the combustion performance of textiles include vertical combustion test method, 45 degree angle test method and so on. Although all these methods can evaluate the burning performance of textiles from different angles, there are still many difficulties for the increasingly developed chemical fiber products and the identification of the flammability of textiles.
Due to the development of synthetic materials, extensive research has been carried out on the determination of the flammability of materials since the 1960s, and the oxygen index method is one of the widely used small-scale test methods. The meaning of the limiting oxygen index is: under the specified test conditions, the zui small capacity percentage of the atmospheric oxygen content required to maintain the combustion of the polymerized material. After two joint tests, the oxygen index method was adopted by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) as a standard test method in 1970, i.e., ASTMD-2863, and since then the method standard has formed the basis of different countries and standards. 1968 Martit first used the oxygen index method for the determination of flammability of textile fabrics, and since then, the oxygen index test method has been accepted by the textile world very quickly, and is widely used in the research work to determine the flammability of textiles. Since then, the oxygen index test method has been accepted by the textile world very quickly and is widely used in research work to determine the flammability of textiles, and the Extreme Oxygen Index Tester is a commonly used test instrument.
Test operation method:
The test is conducted according to GB5454-55. The specimen is to be loaded on the specimen gripper according to the regulations, and then the gripper is inserted into the specimen support in the combustion cylinder. Then open the oxygen, nitrogen valve, adjust the selected flow, with the igniter (adjust the flame height (15-20mm) in the specimen ignition, to confirm the specimen on fire after removing the igniter, and immediately start measuring the specimen combustion time, followed by the determination of the specimen combustion damage length. If the specimen on fire soon after the self-bridging, combustion time of less than 2min or damaged length of less than 40mm, indicating that the oxygen concentration is too low, it must be increased; if the specimen combustion time of more than 2min or combustion damage length of more than 40mm, indicating that the oxygen concentration is too high, it must be reduced. When the adjustment of oxygen or nitrogen flow, and five parallel tests, of which three test results more than the limit value of the burning distance or time, according to the following formula to calculate the oxygen index (LOI) value.
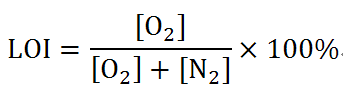
Formula: [O2] for the oxygen flow, L / min, [N2] for the nitrogen flow, L / min
Oxygen index test method can use the relative value to express the flammability performance of fabrics, which is clearer and more explicit. Moreover, the method is more sensitive, so it is one of the valuable test methods to evaluate the flammability of textiles by this method, which can be applied outdoors in the research and production of textile flammability performance.
To determine the flammability of textiles by the oxygen index method, the test conditions such as ambient temperature, humidity and fabric organization and cleanliness will affect the test results. Therefore, the test must be strictly controlled, and the influence of the condition factors should be noted when several textiles are compared.
2023-11-13 13:34